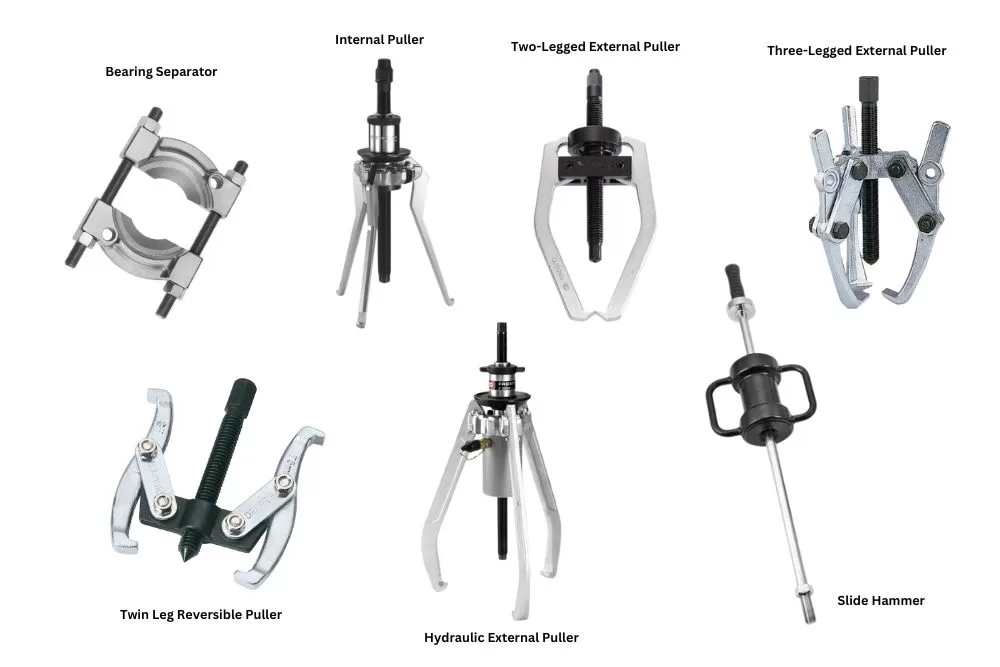
What is a Ball Bearing Puller?
A ball bearing puller is a handy piece of kit to have in your toolbox, especially if you work with machinery and/or vehicles, for instance in the manufacturing or automotive industries.
Bearing pullers are designed to help you to safely and easily remove components such as bearings, pulleys, gears, couplings, and propellers from within or around shafts, in situations where the component cannot be removed by hand.
You’ll find different bearing puller types for different applications, such as internal and external pullers, hydraulic bearing pullers, a wheel bearing puller, and bearing separators.
The key to working with a bearing remover is knowing which tool to select for the job, so here we’ll talk you through the different puller tool types and their main uses.
What are the Components of a Puller?
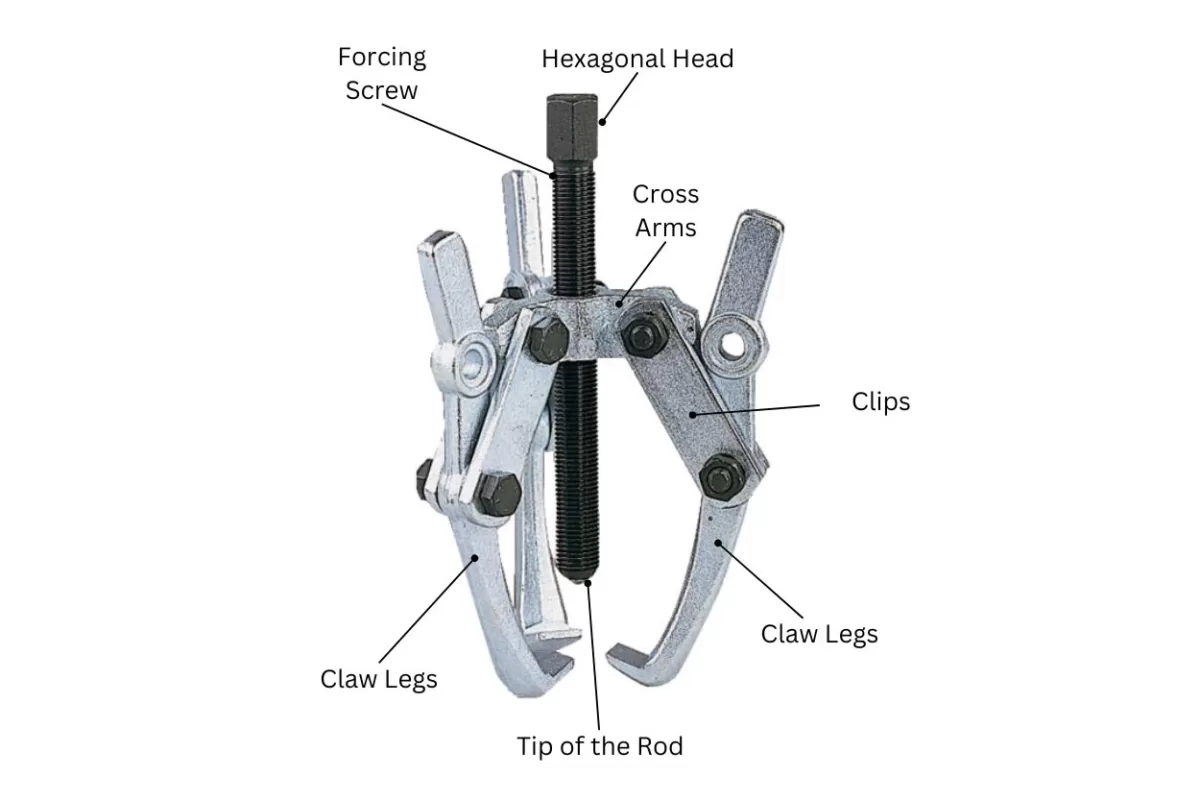
The main components of a bearing removal tool are a hexagonal head, a forcing screw, cross arms, and claw legs.
In fact, bearing pullers share a physical resemblance to the claw of the machines you sometimes see in arcades, where you can win a cuddly toy by correctly lining up and releasing the ‘claw’ in the right location.
Puller Types and Uses
To use a bearing extractor tool correctly, you first need to know the difference between puller types. This is the first step in helping you to identify the correct puller to use for the bearing type you’re working with.
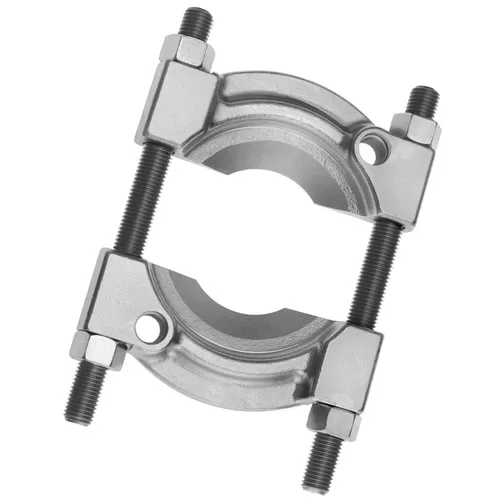
1. Bearing Separator
A separator offers an alternative to an external bearing puller (see further down for more info). They’re mostly called upon when there is limited space behind the bearing, thus making it difficult to grip from behind.
The main feature of a bearing separator is a flat plate with tapered edges. These edges can penetrate the available space and (with the addition of a detachable puller) allow you to move the bearing towards you.
2. Internal Puller
Internal pullers are also known as blind bearing pullers because they extract components from within blind holes or recesses.
As the outside of the component isn’t accessible, an internal puller grips the component from within the bearing’s inner raceway, using collets and an expanding sleeve. Once a firm grip is achieved the bearing can be pulled from within the shaft to bring it out of the recess.
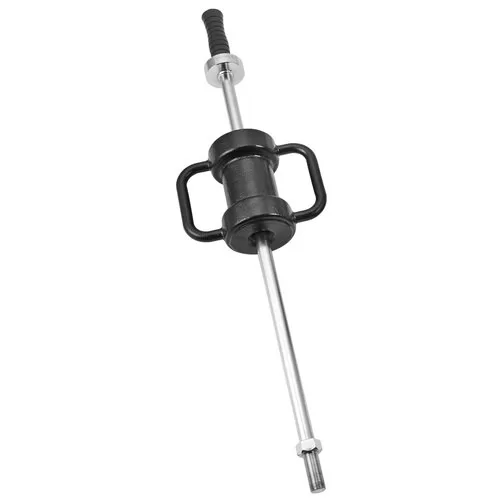
Slide Hammer Bearing Puller
A slide hammer bearing puller features a heavy weight that slides along a shaft that’s machine-threaded at one end and knobbed at the other. Tension is achieved when the sliding weight moves along the shaft to connect with the knob. Unlike other puller types, slide hammer pullers are mostly used to remove dents from automotive vehicles.

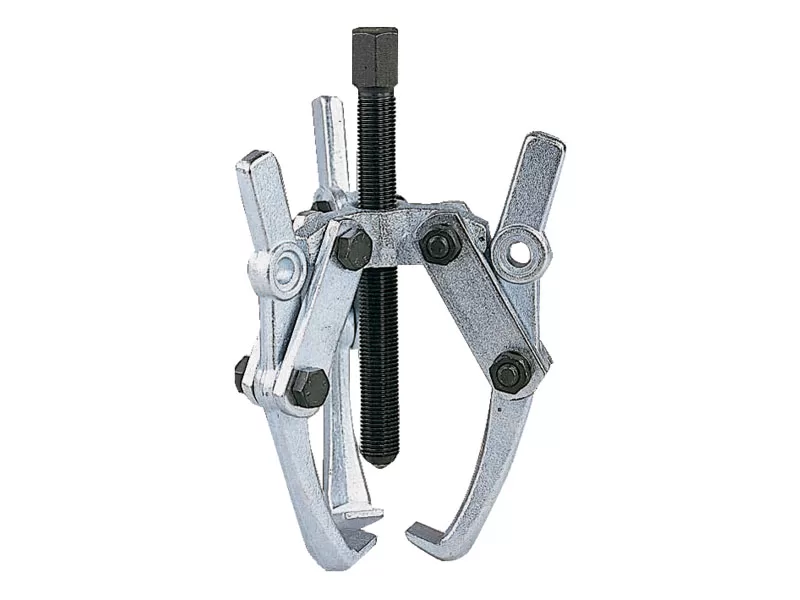
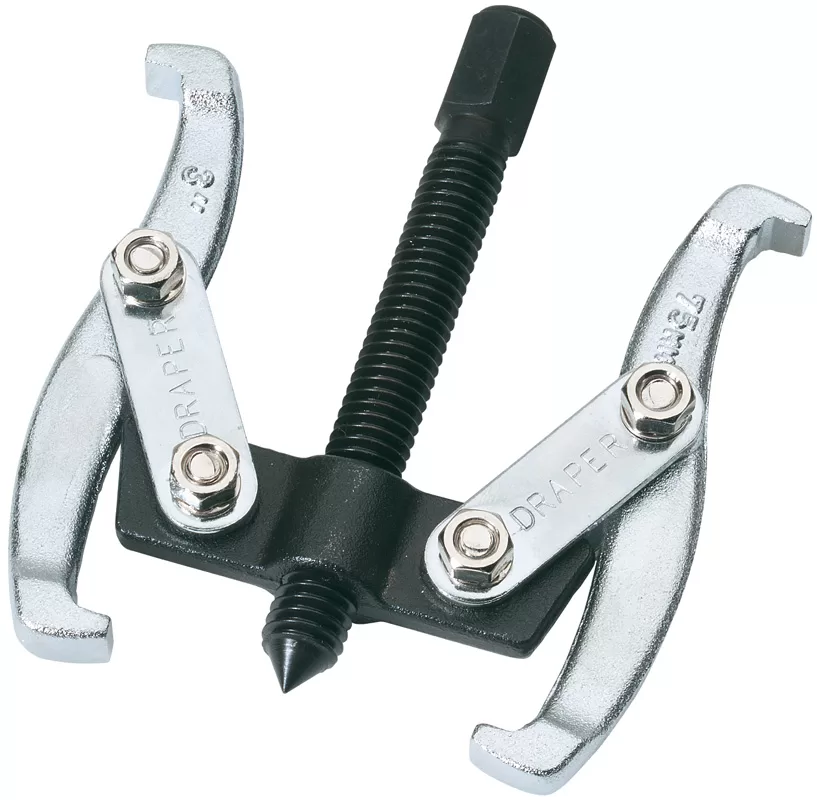
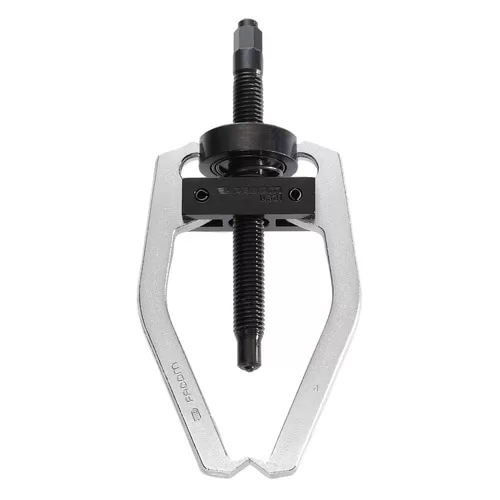
3. External Puller
External pullers are the most common of bearing puller tools. They’re made up of a crossbar, connected to two or three legs (jaws) that grip the bearing, and a central rotating screw that pushes against the shaft.
As external pullers grip from the outside, they’re suited to jobs where the bearing is mounted on a shaft.
Two or three-legged
Whether you use a two or a three-legged external puller depends on the amount of clearance you have around the bearing and how much force you need to apply. Two-legged pullers are more compact and easier to manoeuvre into tight spaces, but three-legged pullers give you a better distribution of force and grip, which helps if the bearing is stuck tight.

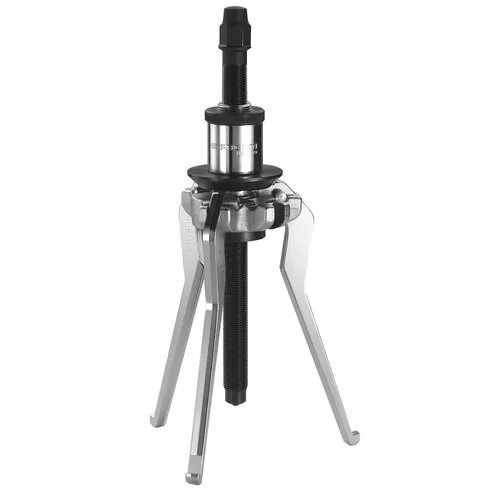
4. Reversible Puller
Reversible bearing pullers have reversible arms that enable them to pull internally and externally.
This means they can remove components that are fitted inside recesses as well as those that are mounted on the outside of a shaft.
5. Hydraulic Bearing Puller
A hydraulic bearing puller is fitted with a pump-powered hydraulic cylinder that uses fluid pressure to remove a bearing from a shaft.
Hydraulic bearing pullers offer the same range of motion as traditional bearing pullers, the only difference being that they are hydraulic powered rather than manually operated. For this reason, you would normally use a hydraulic puller when working with larger bearings.
Features to Consider Before Buying a Puller
Being able to tell the difference between puller types is just one aspect of buying a bearing extractor tool. When it comes to choosing the right puller for the job, you also need to factor is aspects such as reach, spread, legs, material, and bearing size.
- Puller reach, spread, and bearing size
Puller reach refers to the distance between the head of the puller’s legs and the legs’ pulling surface. The puller reach reduces and expands in proportion to how wide or how narrow the legs are open. The spread, meanwhile, is the distance between the jaws at their widest point, which in most bearing pullers is 25 inches. Bearing pullers are also available in a range of sizes, which vary from 75mm (2.9”) all the way up to 200mm (7.8”). When deciding on puller size, it’s important to take into consideration the amount of space or clearance around the shaft or recess, as well as the proportions of the bearing you need to remove.
- Puller type: Two or three-legged
As we briefly touched on earlier, bearing pullers can also be purchased in two-legged or three-legged varieties. Both will enable you to grip the fitting or component you need to remove, and they operate in the exact same way. The key difference between two and three-legged bearing pullers lies in the degree of stability and force. With a two-pronged claw you’re only gripping at opposite sides, so even with locking legs some slippage is possible. With a three-legged puller, you have an additional claw to grip the surface of the component you’re trying to extract, allowing you to distribute the force over a wider area and with a greater degree of stability.
- Safety (material is made of, capacity)
As with all tools, operator safety should be a key consideration when it comes to pullers. To avoid injury, you should always choose a bearing puller that’s manufactured by a reputable brand and made from a high-strength material, robust enough to withstand the tension and pressure you’re putting it under. For hydraulic bearing pullers specifically, it’s vital to ensure that the puller has a 1.5 capacity safety factor and complies with ISO101000:2001.
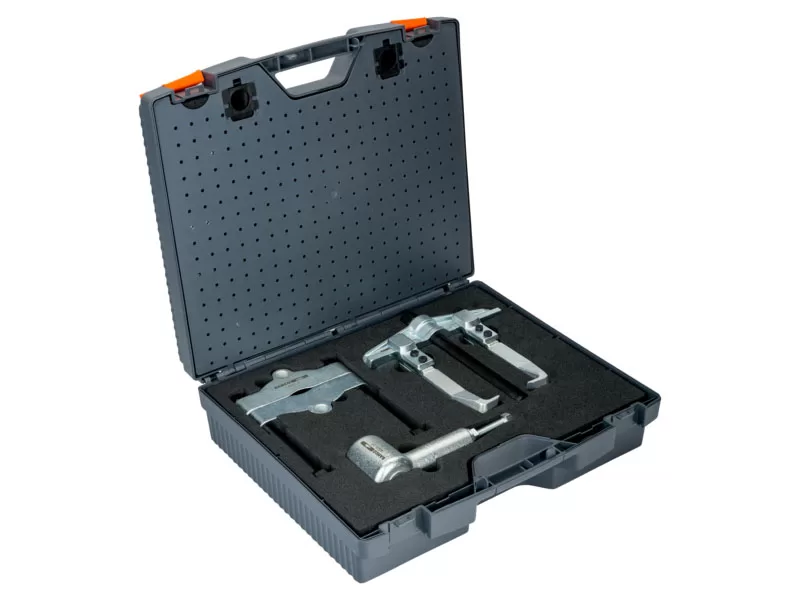
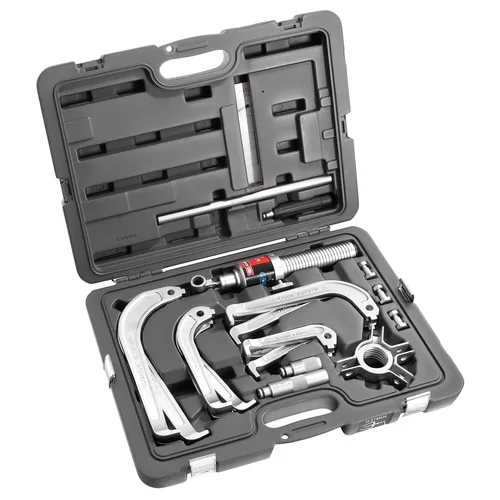
Bearing Puller Sets
Like most tool types, bearing pullers can be purchased individually or as part of a bearing puller tool set. As a rule, you can expect a puller set to include a puller, pump, hose, and pressure gauge. Some bearing puller sets will also include different bearing puller types (external and internal) as well as a bearing separator.
Whether you buy a set or just invest in individual pullers on an ad hoc basis largely depends on the nature of your work and how frequently you require a puller day-to-day.
Popular Bearing Removal Tools
From BAHCO sets made from galvanised steel and three-legged DRAPER models with a 150mm spread, to Lockable FACOM pullers with sliding legs, at Red Box Tools we carry a wide selection of popular puller types, made by trusted brands in tool manufacturing.
Shop our manual and hydraulic bearing pullers on our website today or fulfil all your bearing puller needs at once with a complete bearing puller set in a conveniently portable carry case.
Ready to get organised?
Find your perfect tool storage from our professional range
From tool bags and tool chests to tool boxes with wheels, tool belts, tool cases, and trade-specific tool storage, at Red Box Tools we offer high-quality solutions you can count on.
Or why not take your tool storage to the next level with our made-to-order tool box foam drawer inserts and custom shadow foaming?